In an era dominated by wireless connectivity, the idea of connecting your smartphone to Ethernet might seem unconventional.
However, for those seeking a stable and reliable internet connection, especially for bandwidth-intensive activities like gaming, streaming, or downloading large files, utilizing a wired connection can be a game-changer.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the process of connecting an Ethernet cable to your smartphone, unlocking the potential for faster speeds and reduced latency.
Why Choose Wired Internet for Your Smartphone?
While Wi-Fi is convenient and ubiquitous, it’s susceptible to interference, signal degradation, and congestion, leading to fluctuations in speed and reliability. Wired internet, on the other hand, offers a direct and dedicated connection to your network, bypassing many of the limitations associated with wireless technology. By connecting your smartphone to Ethernet, you can enjoy:
Stability: Wired connections are less prone to interference, ensuring a consistent and stable internet connection.
Speed: Ethernet typically provides faster speeds than Wi-Fi, especially in environments with heavy network traffic.
Lower Latency: Reduced latency is crucial for online gaming and real-time applications, where even milliseconds can make a difference.
Security: Wired connections are generally more secure than Wi-Fi, as they are not susceptible to common wireless security vulnerabilities.
Read: How To Mount a Camera On a Tripod
Connect Ethernet Cable To Smartphone (Wired Internet)
Before connecting your Smartphone to an Ethernet cable, ensure that you have the necessary equipment:
Ethernet Adapter: To connect your smartphone to an Ethernet cable, you’ll need an Ethernet adapter compatible with your device. Consider this one:
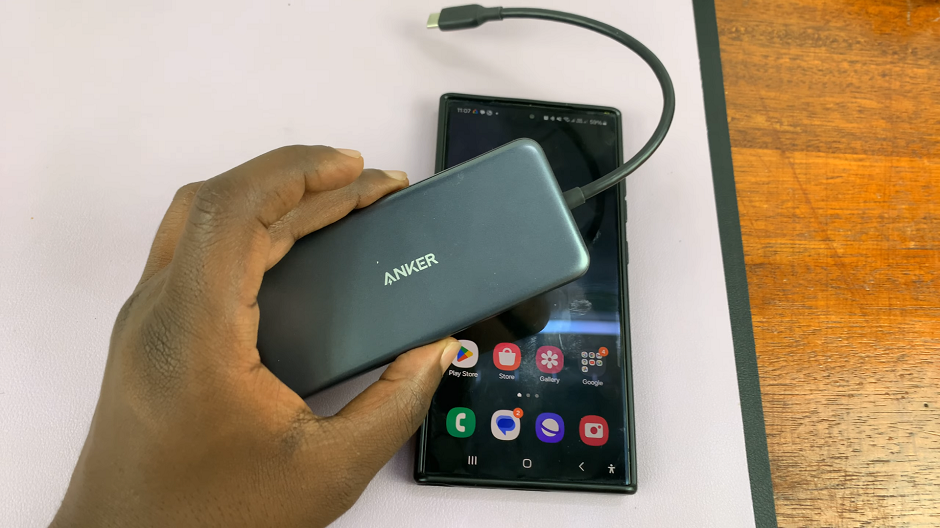

Ethernet Cable: Choose a high-quality Ethernet cable of the appropriate length to connect your smartphone to the router or modem.
Router: Ensure that you have access to a router with an available Ethernet port.
Once you have gathered the necessary equipment, plug one end of the Ethernet adapter into the USB-C port on your smartphone.
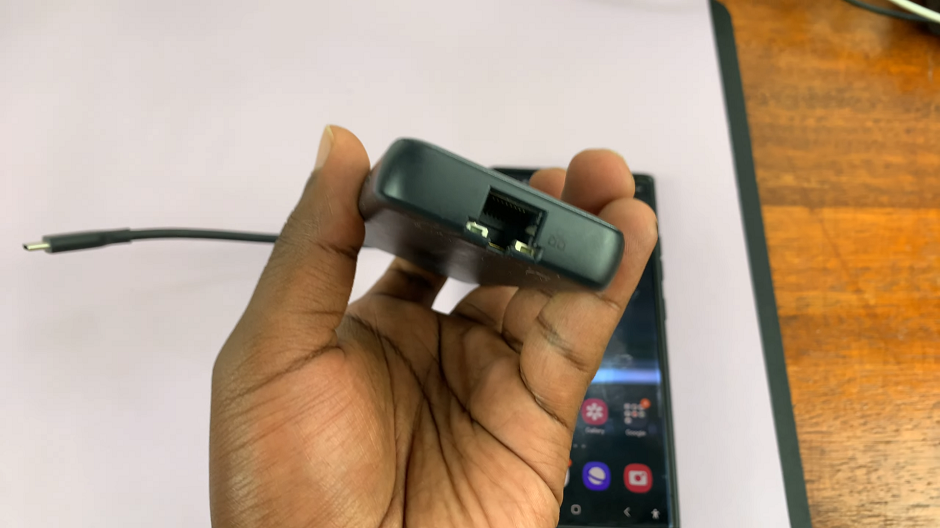

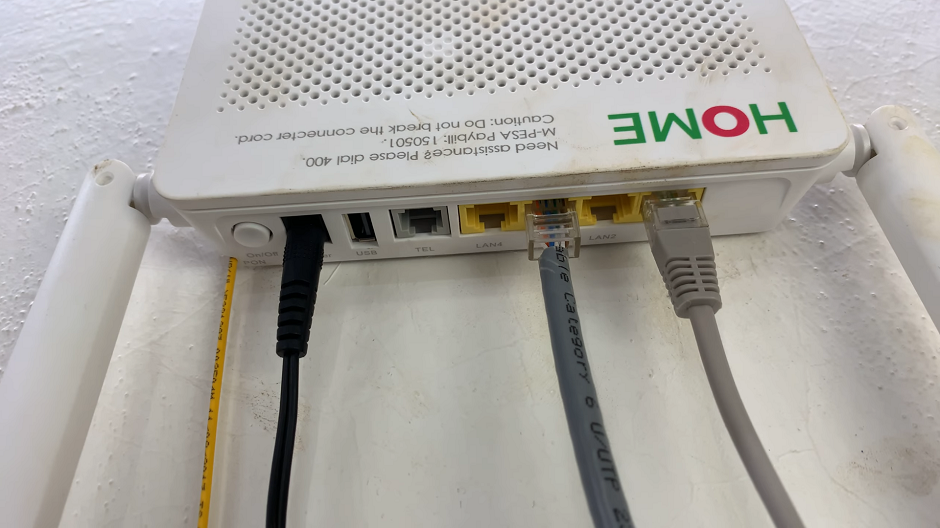
Plug one end of the Ethernet cable into the Ethernet adapter and the other end into an available Ethernet or LAN port on your router or modem.

Upon connecting the Ethernet cable, your smartphone should detect the wired connection automatically. You should also see the end connected to the ethernet adapter blinking to signify connection.
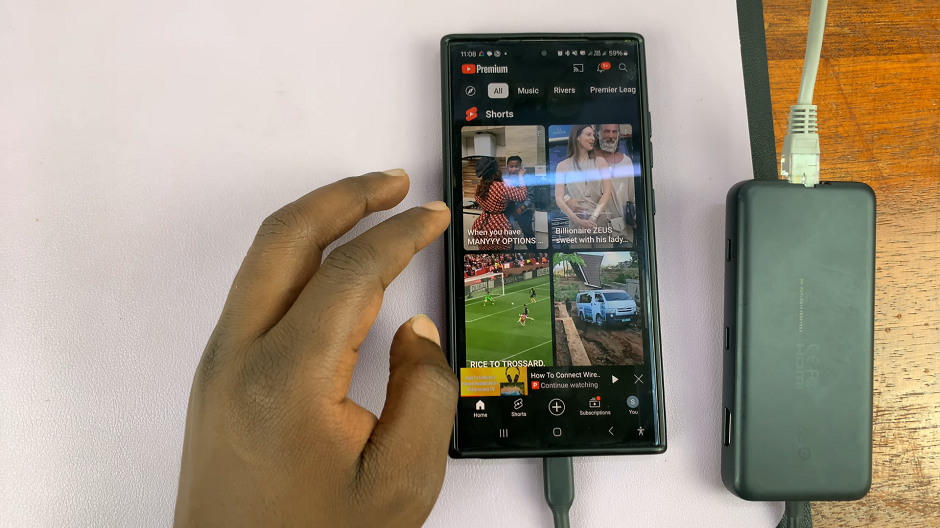

If not, navigate to the Settings menu on your device, select Connections, and then Ethernet. Toggle the switch to enable Ethernet connectivity.
Once enabled, your Smartphone will now be connected to the internet via Ethernet, offering faster speeds and increased stability compared to wireless connections. Disconnect Wi-Fi and Mobile Data to solely use the ethernet cable as your internet link.

Troubleshooting Tips
If your smartphone doesn’t recognize the Ethernet connection, ensure that the adapter is securely connected and that the Ethernet cable is plugged in properly.
Restart your smartphone and router if you encounter any connectivity issues.
Make sure your Ethernet cable and adapter are in good condition, as damaged cables or adapters can cause connectivity issues.
While Wi-Fi remains the go-to option for most smartphone users, connecting your device to Ethernet can offer unparalleled speed, stability, and security. Whether you’re a gamer looking to reduce lag, a streamer craving uninterrupted HD video playback, or a professional needing a reliable internet connection for work, embracing wired internet on your smartphone can elevate your online experience to new heights.